Page 193 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 1
P. 193
Gamze Kazancı Altınok
Finally, natural, free, open-air spaces without constructions in the cities
such as agricultural lands, forests and wetlands etc., which are directly related
to mitigating the effects of climate change, are regarded as reserve areas for
urban growth in the cities, especially in developing countries (Privitera et al,
2018: 820; Bowen et al, 2012: 98). As urban growth is a product of globalization,
the new economy is based on technologically proved service sector. It is known
as one of the reasons for the crisis in agricultural sector, which is seen as a
conventional development method (Privitera et al, 2018: 818). For this reason,
agricultural land and other natural areas are seen as potential urban growth
areas for economic development. (Nichols et al, 2003: 297; Mavrič and Bobek,
2015: 6). However, natural/ open-air spaces serve as not only carbon sink areas
against anthropogenic high carbon emissions, but also as an inhibitor against
the growth of unrecorded settlements in the outskirts of the city. (Masek et al,
2000: 3479; UN-Habitat, 2014: 19).
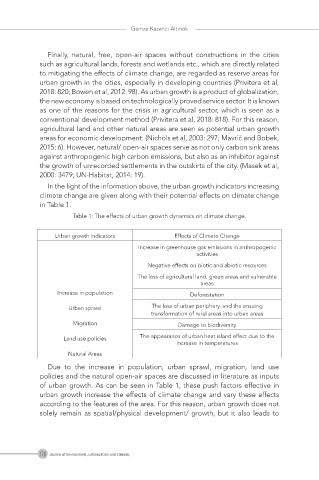
In the light of the information above, the urban growth indicators increasing
climate change are given along with their potential effects on climate change
in Table 1.
Table 1: The effects of urban growth dynamics on climate change.
Urban growth indicators Effects of Climate Change
Increase in greenhouse gas emissions in anthropogenic
activities
Negative effects on biotic and abiotic resources
The loss of agricultural land, green areas and vulnerable
areas
Increase in population Deforestation
Urban sprawl The loss of urban periphery, and the ensuing
transformation of rural areas into urban areas
Migration Damage to biodiversity
Land use policies The appearance of urban heat island effect due to the
increase in temperatures
Natural Areas
Due to the increase in population, urban sprawl, migration, land use
policies and the natural open-air spaces are discussed in literature as inputs
of urban growth. As can be seen in Table 1, these push factors effective in
urban growth increase the effects of climate change and vary these effects
according to the features of the area. For this reason, urban growth does not
solely remain as spatial/physical development/ growth, but it also leads to
178 Journal of Environment, Urbanization and Climate,