Page 199 - Çevre Şehir ve İklim Dergisi İngilizce - Özel Sayı
P. 199
Bilgi Sarihan - Ramazan Acar Çakır
Aydın Uzun
It increases the
osmotic pressure
of the soil solution
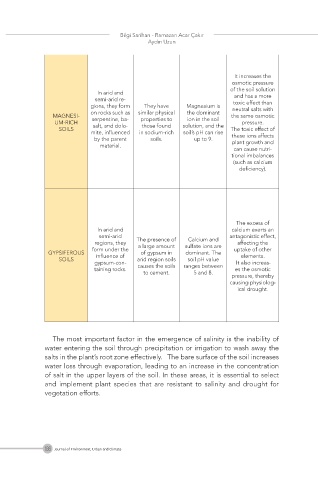
In arid and
semi-arid re- and has a more
toxic effect than
gions, they form They have Magnesium is neutral salts with
on rocks such as similar physical the dominant
MAGNESI- serpentine, ba- properties to ion in the soil the same osmotic
UM-RICH salt, and dolo- those found solution, and the pressure.
SOILS The toxic effect of
mite, influenced in sodium-rich soil’s pH can rise these ions affects
by the parent soils. up to 9. plant growth and
material.
can cause nutri-
tional imbalances
(such as calcium
deficiency).
The excess of
In arid and calcium exerts an
semi-arid antagonistic effect,
regions, they The presence of Calcium and affecting the
form under the a large amount sulfate ions are uptake of other
GYPSIFEROUS influence of of gypsum in dominant. The elements.
SOILS arid region soils soil pH value
gypsum-con- causes the soils ranges between It also increas-
taining rocks. es the osmotic
to cement. 5 and 8.
pressure, thereby
causing physiolog-
ical drought.
The most important factor in the emergence of salinity is the inability of
water entering the soil through precipitation or irrigation to wash away the
salts in the plant’s root zone effectively. The bare surface of the soil increases
water loss through evaporation, leading to an increase in the concentration
of salt in the upper layers of the soil. In these areas, it is essential to select
and implement plant species that are resistant to salinity and drought for
vegetation efforts.
186 Journal of Environment, Urban and Climate