Page 198 - Çevre Şehir ve İklim Dergisi İngilizce - Özel Sayı
P. 198
Use of Climate-Resilient Plants in Arid and Semi-Arid Lands
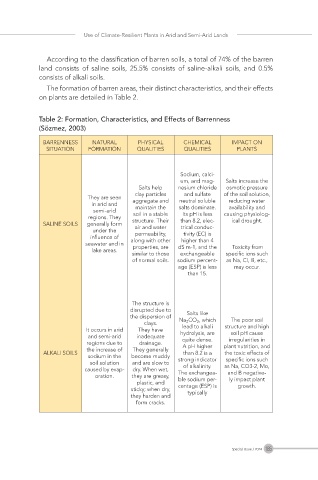
According to the classification of barren soils, a total of 74% of the barren
land consists of saline soils, 25.5% consists of saline-alkali soils, and 0.5%
consists of alkali soils.
The formation of barren areas, their distinct characteristics, and their effects
on plants are detailed in Table 2.
Table 2: Formation, Characteristics, and Effects of Barrenness
(Sözmez, 2003)
BARRENNESS NATURAL PHYSICAL CHEMICAL IMPACT ON
SITUATION FORMATION QUALITIES QUALITIES PLANTS
Sodium, calci-
um, and mag- Salts increase the
Salts help nesium chloride osmotic pressure
clay particles and sulfate of the soil solution,
They are seen aggregate and neutral soluble reducing water
in arid and maintain the salts dominate. availability and
semi-arid
regions. They soil in a stable Its pH is less causing physiolog-
SALINE SOILS generally form structure. Their than 8.2, elec- ical drought.
air and water
trical conduc-
under the
permeability,
tivity (EC) is
influence of along with other higher than 4
seawater and in properties, are dS m-1, and the Toxicity from
lake areas.
similar to those exchangeable specific ions such
of normal soils. sodium percent- as Na, Cl, B, etc.,
age (ESP) is less may occur.
than 15.
The structure is
disrupted due to Salts like
the dispersion of Na₂CO₃, which The poor soil
clays. lead to alkali structure and high
It occurs in arid They have hydrolysis, are soil pH cause
and semi-arid inadequate
irregularities in
regions due to drainage. quite dense. plant nutrition, and
A pH higher
the increase of They generally
ALKALI SOILS than 8.2 is a the toxic effects of
sodium in the become muddy strong indicator specific ions such
soil solution and are slow to
caused by evap- dry. When wet, of alkalinity. as Na, CO3-2, Mo,
oration. they are greasy, The exchangea- and B negative-
ly impact plant
ble sodium per-
plastic, and
sticky; when dry, centage (ESP) is growth.
typically
they harden and
form cracks.
185
Special Issue / 2024