Page 357 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 4
P. 357
Süleyman Toy - Zeynep Eren
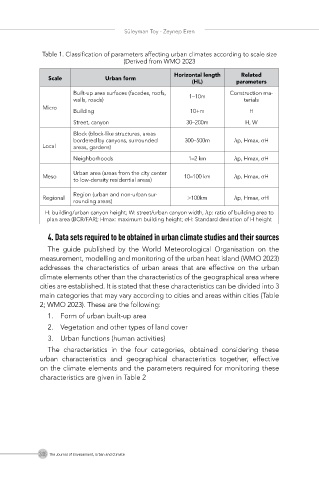
Table 1. Classification of parameters affecting urban climates according to scale size
(Derived from WMO 2023
Horizontal length Related
Scale Urban form
(HL) parameters
Built-up area surfaces (facades, roofs, 1–10m Construction ma-
walls, roads) terials
Micro
Building 10+m H
Street, canyon 30–200m H, W
Block (block-like structures, areas
bordered by canyons, surrounded 300–500m λp, Hmax, σH
Local areas, gardens)
Neighborhoods 1–2 km λp, Hmax, σH
Urban area (areas from the city center
Meso 10–100 km λp, Hmax, σH
to low-density residential areas)
Region (urban and non-urban sur-
Regional >100km λp, Hmax, σH
rounding areas)
H: building/urban canyon height; W: street/urban canyon width, λp: ratio of building area to
plan area (BCR/FAR); Hmax: maximum building height; σH: Standard deviation of H height
4. Data sets required to be obtained in urban climate studies and their sources
The guide published by the World Meteorological Organisation on the
measurement, modelling and monitoring of the urban heat island (WMO 2023)
addresses the characteristics of urban areas that are effective on the urban
climate elements other than the characteristics of the geographical area where
cities are established. It is stated that these characteristics can be divided into 3
main categories that may vary according to cities and areas within cities (Table
2; WMO 2023). These are the following:
1. Form of urban built-up area
2. Vegetation and other types of land cover
3. Urban functions (human activities)
The characteristics in the four categories, obtained considering these
urban characteristics and geographical characteristics together, effective
on the climate elements and the parameters required for monitoring these
characteristics are given in Table 2
346 The Journal of Environment, Urban and Climate