Page 163 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 3
P. 163
Abdüssamet Aydın - Necati Cem Aktuz
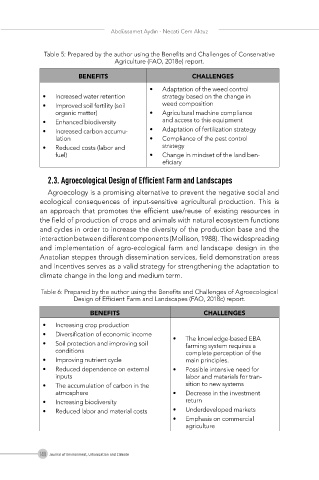
Table 5: Prepared by the author using the Benefits and Challenges of Conservative
Agriculture (FAO, 2018e) report.
BENEFITS CHALLENGES
• Adaptation of the weed control
• Increased water retention strategy based on the change in
• Improved soil fertility (soil weed composition
organic matter) • Agricultural machine compliance
• Enhanced biodiversity and access to this equipment
• Increased carbon accumu- • Adaptation of fertilization strategy
lation • Compliance of the pest control
• Reduced costs (labor and strategy
fuel) • Change in mindset of the land ben-
eficiary
2.3. Agroecological Design of Efficient Farm and Landscapes
Agroecology is a promising alternative to prevent the negative social and
ecological consequences of input-sensitive agricultural production. This is
an approach that promotes the efficient use/reuse of existing resources in
the field of production of crops and animals with natural ecosystem functions
and cycles in order to increase the diversity of the production base and the
interaction between different components (Mollison, 1988). The widespreading
and implementation of agro-ecological farm and landscape design in the
Anatolian steppes through dissemination services, field demonstration areas
and incentives serves as a valid strategy for strengthening the adaptation to
climate change in the long and medium term.
Table 6: Prepared by the author using the Benefits and Challenges of Agroecological
Design of Efficient Farm and Landscapes (FAO, 2018c) report.
BENEFITS CHALLENGES
• Increasing crop production
• Diversification of economic income • The knowledge-based EBA
• Soil protection and improving soil farming system requires a
conditions complete perception of the
• Improving nutrient cycle main principles.
• Reduced dependence on external • Possible intensive need for
inputs labor and materials for tran-
• The accumulation of carbon in the sition to new systems
atmosphere • Decrease in the investment
• Increasing biodiversity return
• Reduced labor and material costs • Underdeveloped markets
• Emphasis on commercial
agriculture
148 Journal of Environment, Urbanization and Climate