Page 160 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 3
P. 160
Ecosystem Based Adaptation Activities to
Climate Change for Sustainable Agriculture
covers different structures such as agricultural afforestation (such as crops,
trees, shrubs), pastoral structures (grassland, animals and trees) and agro-
pastoral structures (crops and grassland /livestock).
Integration of agriculture and forestry reinforces the provision of various
services such as production of food, feed, firewood, improvement and
protection of soil fertility, as well as protection provided by wind barriers and
wind shields. This application supports dynamic, ecologically based natural
resource management. Agroforestry performs natural resource management
by integrating trees/forests into farming systems. In this way, it enables
diversified production to be sustainable by combining more social, economic
and environmental benefits for land beneficiaries at all levels (FAO, 2018b).
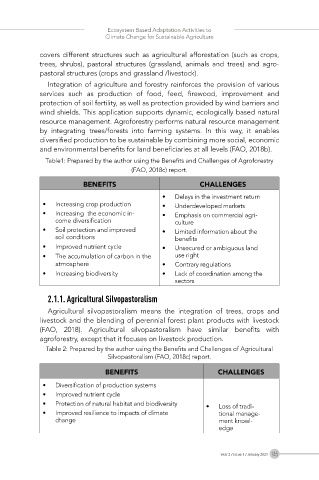
Table1: Prepared by the author using the Benefits and Challenges of Agroforestry
(FAO, 2018c) report.
BENEFITS CHALLENGES
• Delays in the investment return
• Increasing crop production • Underdeveloped markets
• Increasing the economic in- • Emphasis on commercial agri-
come diversification culture
• Soil protection and improved • Limited information about the
soil conditions benefits
• Improved nutrient cycle • Unsecured or ambiguous land
• The accumulation of carbon in the use right
atmosphere • Contrary regulations
• Increasing biodiversity • Lack of coordination among the
sectors
2.1.1. Agricultural Silvopastoralism
Agricultural silvopastoralism means the integration of trees, crops and
livestock and the blending of perennial forest plant products with livestock
(FAO, 2018). Agricultural silvopastoralism have similar benefits with
agroforestry, except that it focuses on livestock production.
Table 2: Prepared by the author using the Benefits and Challenges of Agricultural
Silvopastoralism (FAO, 2018c) report.
BENEFITS CHALLENGES
• Diversification of production systems
• Improved nutrient cycle
• Protection of natural habitat and biodiversity • Loss of tradi-
• Improved resilience to impacts of climate tional manage-
change ment knowl-
edge
Year 2 / Issue 3 / January 2023 145