Page 86 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 1
P. 86
The Role of Carbon Technologies in the
"Net Zero" Target
generation makes up one third of the global CO2 emissions, and the demand
for the sector is increasing every day. The power plants around the World that
run on coal produce 2.000 GW of power in total, and as of 2030, there will
be a 500-GW capacity increase. Today, the natural gas facilities in Asia are 19
years old. Coal-based power plants, on the other hand, are only 12 years old
and they have a financial life-span of decades ahead. If these facilities are not
closed, CCUS technologies may support a fair transition towards a low-carbon
economy (GCCSI, 2020).
In addition, when the role of natural gas in the energy system in the
upcoming decades is considered, CCUS is an important solution to mitigate
CO2 emissions from processing natural gas. Natural gas reserves may
contain CO2 in large amounts, up to 90%, and this CO has to be removed
2
for technical reasons before the gas is dissolved or processed for liquefied
natural gas (LNG) production. The removed CO is typically released into the
2
atmosphere, but could be re-injected into geological formations or used for
EOR. Today, the amount of CO captured in the natural gas processing sector
2
and usually used for EOR is around 26 Mt/year, and this makes up over half the
total amount of captured CO2 (GCCSI, 2021b).
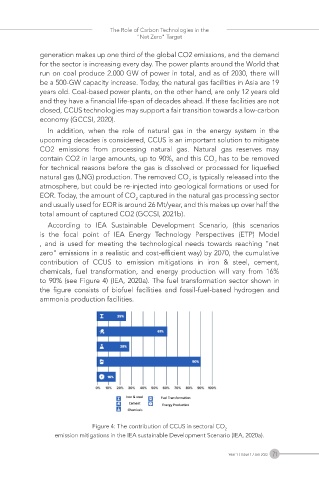
According to IEA Sustainable Development Scenario, (this scenarios
is the focal point of IEA Energy Technology Perspectives (ETP) Model
, and is used for meeting the technological needs towards reaching “net
zero“ emissions in a realistic and cost-efficient way) by 2070, the cumulative
contribution of CCUS to emission mitigations in iron & steel, cement,
chemicals, fuel transformation, and energy production will vary from 16%
to 90% (see Figure 4) (IEA, 2020a). The fuel transformation sector shown in
the figure consists of biofuel facilities and fossil-fuel-based hydrogen and
ammonia production facilities.
Figure 4: The contribution of CCUS in sectoral CO
2
emission mitigations in the IEA sustainable Development Scenario (IEA, 2020a).
Year 1 / Issue 1 / Jan 2022 71