Page 29 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 1
P. 29
Zekâi Şen
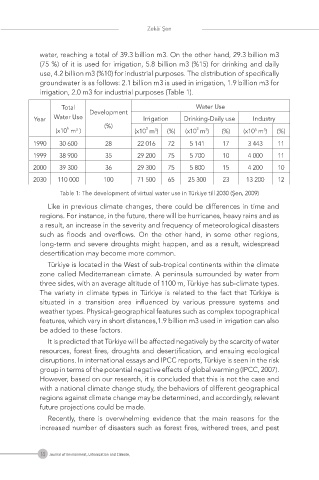
water, reaching a total of 39.3 billion m3. On the other hand, 29.3 billion m3
(75 %) of it is used for irrigation, 5.8 billion m3 (%15) for drinking and daily
use, 4.2 billion m3 (%10) for industrial purposes. The distribution of specifically
groundwater is as follows: 2.1 billion m3 is used in irrigation, 1.9 billion m3 for
irrigation, 2.0 m3 for industrial purposes (Table 1).
Total Development Water Use
Year Water Use Irrigation Drinking-Daily use Industry
(%)
6
3
3
3
(x10 m ) (x10 m ) (%) (x10 m ) (%) (x10 m ) (%)
3
3
3
3
1990 30 600 28 22 016 72 5 141 17 3 443 11
1999 38 900 35 29 200 75 5 700 10 4 000 11
2000 39 300 36 29 300 75 5 800 15 4 200 10
2030 110 000 100 71 500 65 25 300 23 13 200 12
Table 1: The development of virtual water use in Türkiye till 2030 (Şen, 2009)
Like in previous climate changes, there could be differences in time and
regions. For instance, in the future, there will be hurricanes, heavy rains and as
a result, an increase in the severity and frequency of meteorological disasters
such as floods and overflows. On the other hand, in some other regions,
long-term and severe droughts might happen, and as a result, widespread
desertification may become more common.
Türkiye is located in the West of sub-tropical continents within the climate
zone called Mediterranean climate. A peninsula surrounded by water from
three sides, with an average altitude of 1100 m, Türkiye has sub-climate types.
The variety in climate types in Türkiye is related to the fact that Türkiye is
situated in a transition area influenced by various pressure systems and
weather types. Physical-geographical features such as complex topographical
features, which vary in short distances,1.9 billion m3 used in irrigation can also
be added to these factors.
It is predicted that Türkiye will be affected negatively by the scarcity of water
resources, forest fires, droughts and desertification, and ensuing ecological
disruptions. In international essays and IPCC reports, Türkiye is seen in the risk
group in terms of the potential negative effects of global warming (IPCC, 2007).
However, based on our research, it is concluded that this is not the case and
with a national climate change study, the behaviors of different geographical
regions against climate change may be determined, and accordingly, relevant
future projections could be made.
Recently, there is overwhelming evidence that the main reasons for the
increased number of disasters such as forest fires, withered trees, and pest
14 Journal of Environment, Urbanization and Climate,