Page 76 - Çevre Şehir ve İklim Dergisi İngilizce - Özel Sayı
P. 76
The Establishment of New Carbon Sink Areas in Non-Forest Lands and
Carbon Farming in the Process of Climate Change Adaptation
land management technologies and practices can be developed to establish
new CSAs, and the compliance of these areas with carbon crediting and
certification processes can be ensured.
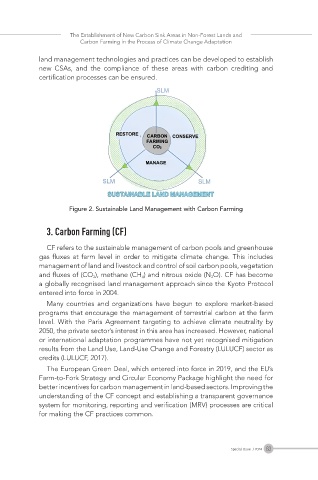
Figure 2. Sustainable Land Management with Carbon Farming
3. Carbon Farming (CF)
CF refers to the sustainable management of carbon pools and greenhouse
gas fluxes at farm level in order to mitigate climate change. This includes
management of land and livestock and control of soil carbon pools, vegetation
and fluxes of (CO₂), methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O). CF has become
a globally recognised land management approach since the Kyoto Protocol
entered into force in 2004.
Many countries and organizations have begun to explore market-based
programs that encourage the management of terrestrial carbon at the farm
level. With the Paris Agreement targeting to achieve climate neutrality by
2050, the private sector’s interest in this area has increased. However, national
or international adaptation programmes have not yet recognised mitigation
results from the Land Use, Land-Use Change and Forestry (LULUCF) sector as
credits (LULUCF, 2017).
The European Green Deal, which entered into force in 2019, and the EU’s
Farm-to-Fork Strategy and Circular Economy Package highlight the need for
better incentives for carbon management in land-based sectors. Improving the
understanding of the CF concept and establishing a transparent governance
system for monitoring, reporting and verification (MRV) processes are critical
for making the CF practices common.
63
Special Issue / 2024