Page 124 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 3
P. 124
Causes of Mucilage Formation and Solution Suggestions in
The Light of Mucilage Composition Findings in The Sea of Marmara
Marmara
Ereğlisi-5
S-5 (mucilage 42 ±1.15 28 ±1.15 14 ±1.15 0.8 ±0.05
zone sea
water)
Mucilage
S-11 (Solid 43 ±1.15 4 ±1.15 39 ±1.15 3.2 ±0.05
Matter) (TKN)
The S-3 sample is a mucilage sample, where total carbon (TC= 428 ppm),
inorganic carbon (IC= 93.8 ppm), total organic carbon (TOC=334.2 ppm) and
total nitrogen (TN=17 ppm) were obtained as indicated (Table 1).
According to the analyses, sea snot has a structure consisting mostly of
organic matter and water. Due to the its high organic matter content, mucilage
was compared to the structure of the aleo vera plant, which has a mucilaginous
liquid in its structure (Table 1). The structure of the mucilage-like jelly part of the
aleo vera plant contains total carbon (TC= 866 ppm), inorganic carbon (IC= 11
ppm), total organic carbon (TOC=855 ppm) and total nitrogen (TN=17 ppm)
(Yümün and Kam, 2021). The total carbon and organic carbon values detected
in aleo vera mucilage are higher than in marine mucilage, while the nitrogen
value is similar in both mucilages. These findings indicate that sea snot is of
organic origin and is a secretion produced by algae and other phytoplankton.
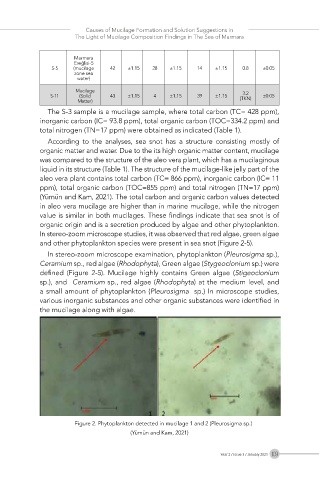
In stereo-zoom microscope studies, it was observed that red algae, green algae
and other phytoplankton species were present in sea snot (Figure 2-5).
In stereo-zoom microscope examination, phytoplankton (Pleurosigma sp.),
Ceramium sp., red algae (Rhodophyta), Green algae (Stygeoclonium sp.) were
defined (Figure 2-5). Mucilage highly contains Green algae (Stigeoclonium
sp.), and Ceramium sp., red algae (Rhodophyta) at the medium level, and
a small amount of phytoplankton (Pleurosigma sp.) In microscope studies,
various inorganic substances and other organic substances were identified in
the mucilage along with algae.
Figure 2. Phytoplankton detected in mucilage 1 and 2 (Pleurosigma sp.)
(Yümün and Kam, 2021)
Year 2 / Issue 3 / January 2023 109