Page 99 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 2
P. 99
Burcu Hiçyılmaz - Sedat Alataş - Etem Karakaya
importance and potential of material efficiency in terms of mitigation policies,
respectively. The third part investigates the scope of the product life cycle and
the material strategies suitable for each stage, while the fourth part evaluates
and discusses the findings and concludes.
1. Industry, Mitigation Options and Material Efficiency
a. Industrial Emissions
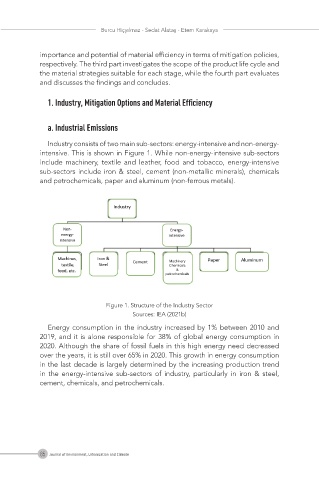
Industry consists of two main sub-sectors: energy-intensive and non-energy-
intensive. This is shown in Figure 1. While non-energy-intensive sub-sectors
include machinery, textile and leather, food and tobacco, energy-intensive
sub-sectors include iron & steel, cement (non-metallic minerals), chemicals
and petrochemicals, paper and aluminum (non-ferrous metals).
Machinery
Chemicals
&
petrochemicals
Figure 1. Structure of the Industry Sector
Sources: IEA (2021b)
Energy consumption in the industry increased by 1% between 2010 and
2019, and it is alone responsible for 38% of global energy consumption in
2020. Although the share of fossil fuels in this high energy need decreased
over the years, it is still over 65% in 2020. This growth in energy consumption
in the last decade is largely determined by the increasing production trend
in the energy-intensive sub-sectors of industry, particularly in iron & steel,
cement, chemicals, and petrochemicals.
85 Journal of Environment, Urbanization and Climate