Page 269 - Çevre Şehir İklim İngilizce - Sayı 3
P. 269
Cihan Erçetin
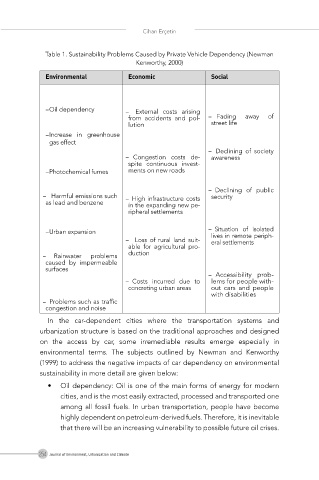
Table 1. Sustainability Problems Caused by Private Vehicle Dependency (Newman
Kenworthy, 2000)
Environmental Economic Social
- Oil dependency - External costs arising
from accidents and pol- - Fading away of
lution street life
- Increase in greenhouse
gas effect
- Declining of society
- Congestion costs de- awareness
spite continuous invest-
- Photochemical fumes ments on new roads
- Declining of public
- Harmful emissions such - High infrastructure costs security
as lead and benzene in the expanding new pe-
ripheral settlements
- Urban expansion - Situation of isolated
lives in remote periph-
- Loss of rural land suit- eral settlements
able for agricultural pro-
- Rainwater problems duction
caused by impermeable
surfaces
- Accessibility prob-
- Costs incurred due to lems for people with-
concreting urban areas out cars and people
with disabilities
- Problems such as traffic
congestion and noise
In the car-dependent cities where the transportation systems and
urbanization structure is based on the traditional approaches and designed
on the access by car, some irremediable results emerge especially in
environmental terms. The subjects outlined by Newman and Kenworthy
(1999) to address the negative impacts of car dependency on environmental
sustainability in more detail are given below:
• Oil dependency: Oil is one of the main forms of energy for modern
cities, and is the most easily extracted, processed and transported one
among all fossil fuels. In urban transportation, people have become
highly dependent on petroleum-derived fuels. Therefore, it is inevitable
that there will be an increasing vulnerability to possible future oil crises.
254 Journal of Environment, Urbanization and Climate