Page 252 - Çevre Şehir ve İklim Dergisi İngilizce - Özel Sayı
P. 252
Footprints of the Nature in Cities; Urban Heat Island Effects
and the Role of Afforestation Efforts in Reduction of These Effects
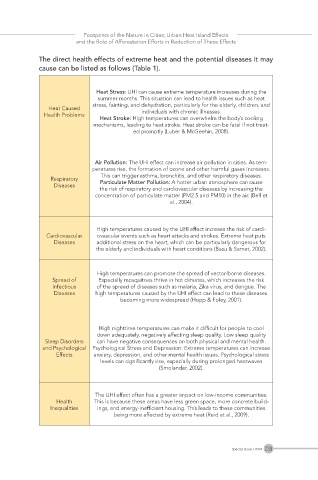
The direct health effects of extreme heat and the potential diseases it may
cause can be listed as follows (Table 1).
Heat Stress: UHI can cause extreme temperature increases during the
summer months. This situation can lead to health issues such as heat
stress, fainting, and dehydration, particularly for the elderly, children, and
Heat Caused
Health Problems individuals with chronic illnesses.
Heat Stroke: High temperatures can overwhelm the body’s cooling
mechanisms, leading to heat stroke. Heat stroke can be fatal if not treat-
ed promptly (Luber & McGeehin, 2008).
Air Pollution: The UHI effect can increase air pollution in cities. As tem-
peratures rise, the formation of ozone and other harmful gases increases.
This can trigger asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory diseases.
Respiratory Particulate Matter Pollution: A hotter urban atmosphere can rause
Diseases
the risk of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases by increasing the
concentration of particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) in the air. (Bell et
al., 2004).
High temperatures caused by the UHI effect increase the risk of cardi-
Cardiovascular ovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. Extreme heat puts
Diseases additional stress on the heart, which can be particularly dangerous for
the elderly and individuals with heart conditions (Basu & Samet, 2002).
High temperatures can promote the spread of vector-borne diseases.
Spread of Especially mosquitoes thrive in hot climates, which increases the risk
Infectious of the spread of diseases such as malaria, Zika virus, and dengue. The
Diseases high temperatures caused by the UHI effect can lead to these diseases
becoming more widespread (Hopp & Foley, 2001).
High nighttime temperatures can make it difficult for people to cool
down adequately, negatively affecting sleep quality. Low sleep quality
Sleep Disorders can have negative consequences on both physical and mental health.
and Psychological Psychological Stress and Depression: Extreme temperatures can increase
Effects anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Psychological stress
levels can significantly rise, especially during prolonged heatwaves
(Smolander, 2002).
The UHI effect often has a greater impact on low-income communities.
Health This is because these areas have less green space, more concrete build-
Inequalities ings, and energy-inefficient housing. This leads to these communities
being more affected by extreme heat (Reid et al., 2009).
239
Special Issue / 2024